

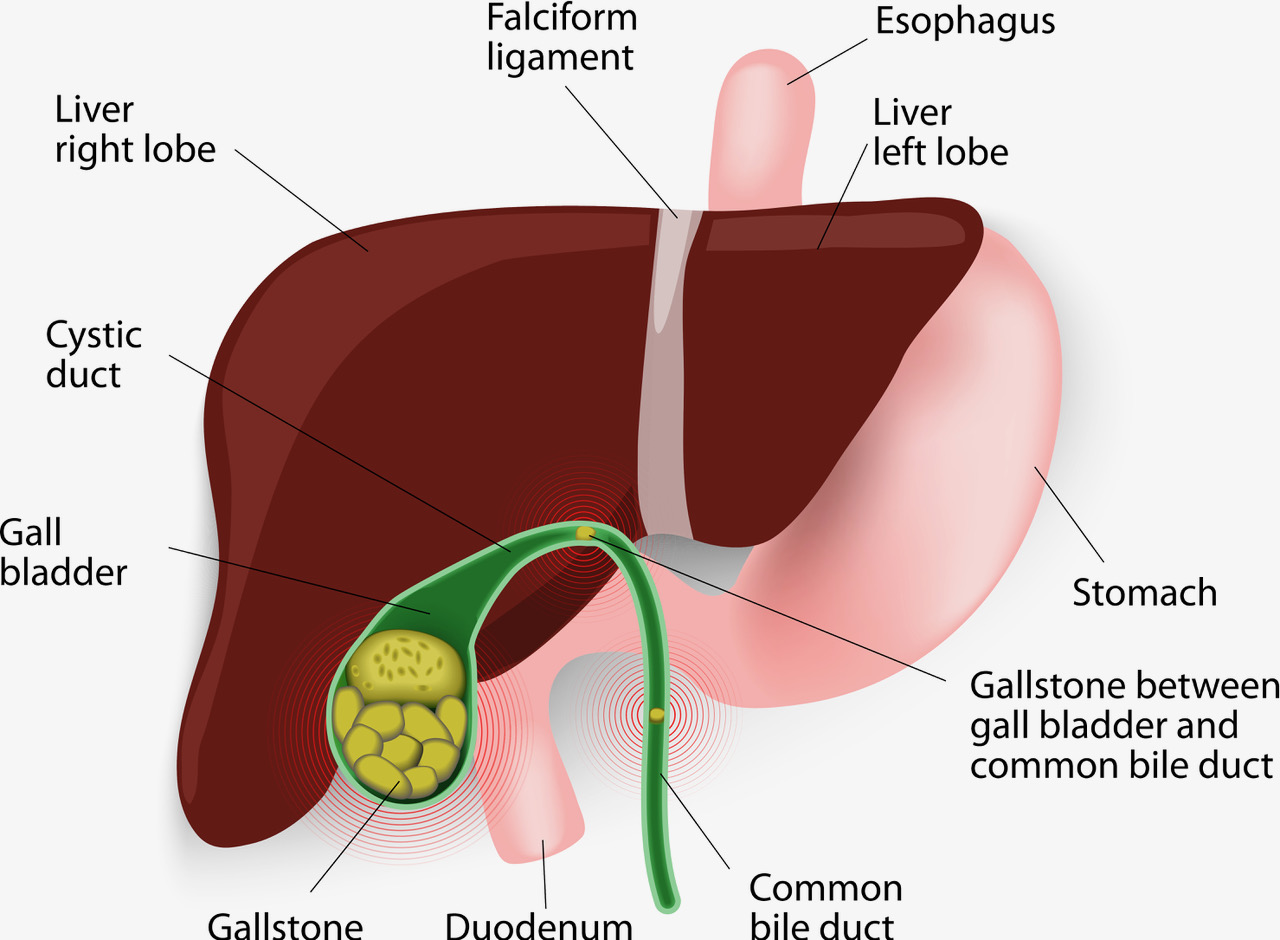
Gallstones are hard, pebble-like pieces of material, usually made of cholesterol or bilirubin, that form in your gallbladder. Gallstones can range in size from a grain of sand to a golf ball. The gallbladder can make one large gallstone, hundreds of tiny stones, or both small and large stones.
When gallstones block the bile ducts of your biliary tract, the gallstones can cause sudden pain in your upper right abdomen. This pain is called a gallbladder attack, or biliary colic. If your symptoms continue and they’re left untreated, gallstones can cause serious complications.
However, most gallstones don’t cause blockages and are painless, also called “silent” gallstones. Silent gallstones usually don’t need medical treatment.
The two main types of gallstones are
Cholesterol stones are usually yellow-green in color and are made of mostly hardened cholesterol. In some countries, cholesterol stones make up about 75 percent of gallstones.1
Pigment stones are dark in color and are made of bilirubin. Some people have a mix of both kinds of stones.
Your biliary tract, which is made up of your gallbladder and bile ducts, helps with digestion by releasing bile.
The gallbladder is a small, pear-shaped organ that stores bile and is located in your upper right abdomen, below your liver.
The bile ducts of your biliary tract include the hepatic ducts, common bile duct, and cystic duct. Bile ducts also carry waste and digestive juices from the liver and pancreas to the duodenum.
Your liver produces bile, which is mostly made of cholesterol, bile salts, and bilirubin. Your gallbladder stores the bile until it’s needed. When you eat, your body signals your gallbladder to empty bile into your duodenum to mix with food. The bile ducts carry the bile from your gallbladder to the duodenum.
Gallstones are very common, affecting 10 to 15 percent of the U.S. population, which is almost 25 million people. About a quarter of the nearly 1 million people diagnosed with gallstones each year will need to be treated, usually with surgery.2
Certain groups of people have a higher risk of developing gallstones than others.3
You are more likely to develop gallstones if you have one of the following health conditions:
You are more likely to develop gallstones if you
Learn more about dieting and gallstones.
Complications of gallstones can include
Many people do not have symptoms of gallstones until they have complications.
If left untreated, gallstones can be deadly. Treatment for gallstones usually involves gallstone surgery.





Contact Us
Covina Location
500 W. San Bernardino Rd, Suite B Covina, CA 91722
(626) 960-2326
Glendora Location
415 W. Route 66, Suite 102 Glendora, CA 91740
(626) 610-2112